I'm looking for information about
Can't find what you're looking for? You may need to login to see more documents
Suggested parameters and sets of instructions outlining best practices and standards for accomplishing specific duties.
This Copy Was Generated On: July 11, 2025
Secondary Use Research
IRBMED
| Approval Date:
August 14, 2023 11:45 am
Secondary Use research is subject to IRB oversight if investigators “obtain identifiable private data or identifiable biospecimens.” This is because the regulatory definition of “human subjects research” is met whenever an investigator obtains, uses, or generates identifiable private information or identifiable biospecimens. “Identifiable” refers to:
- When the Common Rule applies, information for which identity of the subject is or may readily be ascertained by the investigator or associated with the information
- When HIPAA applies, private information which contains any of the 18 HIPAA direct or indirect identifiers.
Among other things, the IRB must consider how proposed secondary uses of data or biospecimens meet applicable regulatory requirements for informed consent. Informed consent obtained at the time of data/specimen collection often does not imply consent for (future) secondary research uses via a “Pre-existing Consent…”.
NOTE: If Secondary use is paired with subject interaction or intervention, a Secondary Use application type is no longer applicable. In this case, choose “Human Subjects research involving interaction or intervention…” as the application type in Section 01-1.
DEFINITIONS
NOTE: for any words or phrases that have a link with a magnifying glass icon, hovering over the term will pop up a more detailed definition.
Secondary uses are analyses to investigate new research question(s), whether conducted by the investigator who initially acquired the data/biospecimens or by any other investigator. An investigator can propose research analysis of retrospective (already existing) and/or prospective (yet to be generated) materials, including those obtained through clinical care.
Primary uses are those specific uses for which data/biospecimens were initially acquired. For the Electronic Medical Record (EMR), the primary use is clinical care. Research analysis of data/biospecimens is “primary use” if it is part of the research project for which the data/biospecimens were collected.
Coded dataset: Per OHRP guidance, means that:
- identifying information (such as name or social security number) that would enable the investigator to readily ascertain the identity of the individual to whom the private information or specimens pertain, has been replaced with a number, letter, symbol, or combination thereof (i.e., the code); and
- a key to decipher the code exists, enabling linkage of the identifying information to the private information or specimens. This is regardless of who holds the key to decipher the code.
Engagement in research (for purposes of secondary use research): A performance site is deemed to be engaged in human research when it receives a direct grant or other award to support the research or obtains individually identifiable private information for purposes of the research.
Examples of non-engagement in UM human subjects research: Primary analysis of de-identified or coded information obtained for research purposes at other institutions or releasing identifiable private information or biological specimens (such as from a repository).
HIPAA-specific terms
HIPAA Identifiers: Protected Health Information (PHI) includes at least one of a list of 18 defined HIPAA Identifiers. Most of these are considered direct Identifiers. A few are considered Indirect Identifiers: these are permissible in a HIPAA Limited Data Set.
Covered Entity: a health care provider, health plan, or health care clearinghouse regulated by HIPAA.
Limited Data Set: HIPAA indirect identifiers (involving locations, dates, and subject ID codes) are included. No other HIPAA identifiers are permitted in a limited data set.
De-identified dataset: for HIPAA purposes, this most often means that all 18 types of HIPAA identifiers have been removed. The dataset is no longer considered regulated by HIPAA (unless it is later re-identified). Discussion and further details at Research A-Z page De-identified Data Sets.
I. eResearch Application
The following two application types are available in Section 1-1.1 of eResearch application for research that will be using secondary use of private information and specimens: “Secondary research uses of private information and/or biospecimens,” and “Activities not-regulated as human subjects research.”
The eResearch application type “Secondary research uses… ” triggers a “Scope of Secondary Use Research” (Section 01-1.2) to be completed by the study team. This “scope” section is designed to route the application to the appropriate IRB review and determination path (i.e., Not Regulated, Exempt, or comprehensive IRB review) for all secondary use studies.
The eResearch application type “Activities not regulated…” in Section 1-1.1 will route the application to Section 04-1 (Not Regulated sub-categories). Once submitted, IRBMED will determine if the proposed activity meets criteria for a Not-Regulated determination and if a limited review by IRBMED is required.
A. Not Regulated
A Not Regulated determination may apply if
- the researchers doing the analysis do not at any point have the ability to “re-identify” the data/biospecimens, or the study involves only information on deceased individuals. These studies are not regulated as human subject research per definition of “human subjects” by 45 CFR 46.102.
- the project is not considered to be “research” by 45CFR46.102. Certain categories such as quality improvement/quality assurance, case studies, and pre-review of clinical data sets preparatory to research, are not designed to contribute to “generalizable knowledge” and may fit into this category. (See Section 1-1.1 of eResearch for more information.)
Not all Not Regulated activities require an IRB application. The U-M HRPP Operations Manual (Part 4 Activities Subject to the HRPP & table 5 on page 43) describes the scenarios for which an IRB application is required.
Once a Not Regulated IRB application is submitted, a limited IRBMED review is sometimes required to assess compliance with HIPAA or other regulations. In other words, while a project may be Not-Regulated under human subject research regulations, it may still need to comply with HIPAA privacy regulations, and that is what IRBMED will need to assess in a limited review.
B. Exempt Human Subjects Research
An Exemption, per Category 4, applies to most secondary use research studies limited to retrospective and/or prospective collection of data/biospecimens, such as the use of:
- 4(i), public data sources such as the phone book (uncommon at Michigan Medicine);
- 4(ii), non-public data/biospecimens sources if study team will not record any direct or indirect identifiers and will not contact the subjects (common at Michigan Medicine), or
- 4(iii), when all data are regulated by HIPAA and all study team members, and their institutions are part of a HIPAA covered entity (CE). This is common when all study team members and activity occurs within Michigan Medicine.
- The reason that data must be kept/shared within a HIPAA CE for the Exempt 4(iii) determination is that the PHI needs to be kept secure. HIPAA covered entities require HIPAA-compliant data storage systems and member training to ensure PHI is not disclosed outside of HIPAA regulations. Research teams sharing data outside of a HIPAA CE must explain how they will protect patient PHI from improper use or disclosure in a comprehensive IRB review.
- When biospecimen analysis with HIPAA identifiers is involved, the study is not eligible for an Exempt 4(iii) determination; it will require a comprehensive IRB review. Biospecimens without any identifiers do not need a waiver of HIPAA authorization because HIPAA pertains to information only.
C. Comprehensive IRB Review and Approval
Comprehensive IRB review and approval (according to all regulatory criteria at 45 CFR 46.111) is required when “Not Regulated” and “Exempt” are not applicable. Examples include (Question numbers refer to Section 01-1.2):
- Research dataset analysis which includes identifiable private information not covered under HIPAA. (Question 8.1)
- Certain research that includes biospecimens (Question 8.1)
- The data/biospecimen provider requires full or expedited IRB review (e.g. some dbGaP datasets, based on Data Use Certification) (Question 2)
- Data are intended for IDE (Investigational Device Exemption) or In Vitro Diagnostic (IVD) device application to FDA (Question 5)
Question 5.8 in Section 05 of the IRB application will ask if there are additional risks not related to breach of confidentiality. Rarely, a secondary use study may have a risk level determined as greater than minimal.

TIPS for eResearch Secondary Use applications
- Section 24/44: IRBMED will need to know the specific data/variables collected from the data sources in order to confirm the specific regulatory review pathway. This is usually fulfilled by the study team by providing a data collection sheet in Section 24 or 44. The data collection sheet (aka Data Dictionary) should identify the data variables collected from each data source. Alternatively, this information can be provided within the IRB application (within one of the free text fields in 01.8 Project Summary or the study protocol).
- Question 24.3: State clearly what PHI data elements will be recorded from the data sets. Many study teams are unclear about the terms “de-identified”, “limited data set”, and “coded.” For example, if a subject’s name and MRN number are recorded, even on a separate spreadsheet from the study data, then subject identifiers are being recorded and the data set is not de-identified. If dates (other than year) are in the data set, then the data set is not de-identified. (See IRBMED FAQ.) If both direct identifiers and a coding system is used, then select both “direct identifiers” and “coded or indirect identifiers in Q 24.4.
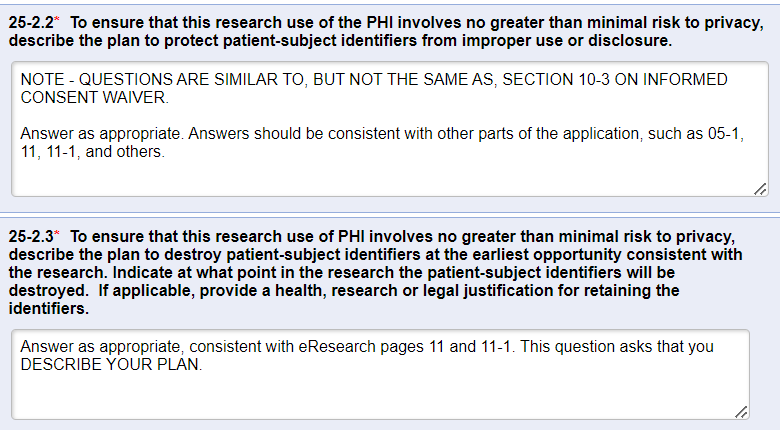
- Question 25-2.2: A “best-practice” recommendation is to code the data when conducting data analysis, whereby a subject ID code would be added to the file instead of the subject’s name, MRN, or other direct identifier. Direct identifiers with the link to the code should be minimally necessary and stored in a password-protected, HIPAA-compliant file that is in a separate location from the study data file. That way, if the data file is printed or shared, it protects subject identifiers from improper use and/or disclosure.
- Question 25-2.3: When the data analysis is FULLY complete (including journal acceptance, if applicable), ALL stored data should be stripped of identifiers (direct and indirect) in order to create a FULLY de-identified data set that is no longer regulated under federal regulations or by U-M’s HRPP. It is not necessary to delete all study data, but all 18 HIPAA identifiers must be deleted from the data set once the study has been completed unless there is a valid reason to retain subject identifiers. Dates can be replaced with the year only in a de-identified data set.
II. Non-identifiable Materials
Secondary Use research generally will not require IRB oversight if investigators receive only data that are ‘de-identified’ (data that cannot be re-identified by ANYONE, link/key to the data has been destroyed) or ‘coded’ (investigators do not have access to the link/key but it still exists). Based on responses in the “Scope of Secondary Use Research” Section (01-1.2) , eResearch may route these applications to the “Research Not Regulated by the IRB” Section (04-1) . Then, select one of the following applicable Not Regulated categories:
- Research Involving Coded Private Information. Provide details on data access in Section 24; HIPAA review may be required.
- Research Involving Coded Biological Specimens. Provide details regarding specimens in Section 18.
- Research Involving De-identified Biological Specimens or Information (“de-identified” i.e., re-identification is not possible by any known entity). Describe how specimens or information are de-identified in Section 1.8 or in the uploaded protocol.
- Activities not engaging UM in human subject research. Choose when there is cooperative research with investigators from another institution and U-M is not engaged in the research per the regulatory definition.
NOTE: If investigators have the ability to “re-identify” data or biospecimens, then the materials are considered “identifiable” and IRB oversight is required. See Section I for comprehensive IRB review.
Special Situation: U-M as data PROVIDER only
When U-M’s role on the study is LIMITED TO using full PHI to prepare a dataset for analysis by external site researchers, and the data sent outside U-M is NOT considered “individually identifiable,” choose “Activities not regulated…” in application type 01-1. Per OHRP 2008 Guidance, this activity is “Research Involving Coded Private Information (Q4-1.1)” where U-M’s role is the “data provider” and the “investigators” (external to U-M) cannot readily ascertain the identity of the individual(s) to whom the coded private information or specimens belong.
Special Situation: Obtaining data/specimens through an “honest broker”
U–M researchers receiving data/specimens without identifiable data through an ‘honest broker’, either from an internal source (e.g. DataDirect, Central Biorepository, Tissue Procurement Service) or an external source (e.g. dbGaP, BioLINCC or CMS-ResDAC) should choose either the “Secondary research…” or “Activities Not Regulated…” application type in Section 01-1. Some data sources that contain sensitive or genetic information will require IRB oversight; selecting either of these should route the application to the appropriate section.
Special Situation: Research to support an investigational device exemption (IDE) through the FDA
If de-identified specimens are used to develop data that will be submitted to the FDA as part of an IDE application, the Secondary research use application must be completed. Answer “yes” to question #5 in Section 1-1.2 (“Will data from the proposed activity be submitted in an application to the FDA for an IDE (Investigational Device Exemption) or In Vitro Diagnostic (IVD) device approval?”).
III. Sharing Michigan Medicine Data/Biospecimens
When data/biospecimens are shared for research purposes with non-U-M entities (“outgoing” from U-M), a formal Unfunded Agreement (UFA) should be in place, even if the data are HIPAA-de-identified. UFA applications can be completed through eResearch Proposal Management; the UFA number, even if in progress, should be added to Section 2 of the IRBMED application. The two main types of these agreements are:
- Data Use Agreement (DUA) or Data Sharing Agreement (DSA): The DUA category can be selected for data outgoing from the University of Michigan or incoming to the University of Michigan. For assistance starting the UFA, contact the primary research administrator for your unit. Coordination with the primary research administrator is recommended to ensure that accurate data elements are conveyed in the DUA. Faculty, chairs, and departmental administrators do not have the authority to sign these agreements on behalf of the University.
- Materials Transfer Agreement (MTA) or Data and Materials Distribution Agreement (DMDA): The MTA category can be selected for materials outgoing from the University of Michigan or incoming to the University of Michigan. For assistance setting up a MTA, contact Innovation Partnerships at UM, via email: [email protected]. This unit must be involved with MTA negotiations for both incoming and outgoing biospecimens. Faculty, chairs, and departmental administrators do not have the authority to sign these agreements on behalf of the University.
Special Situation: Transfer to Industry
The transfer of Michigan Medicine individual-level data and biospecimens (not part of a clinical trial) to industry or non-academic and non-governmental entities may also require review and approval by the Medical School Human Data & Biospecimen Release Committee. See Data & Biospecimen Sharing webpage. For assistance, contact the Data Office for Clinical & Translational Research (DOCTR).
IV. Prior Consent for Secondary Use Research
A. Consent and HIPAA Authorization Considerations for Identifiable Data/Biospecimens
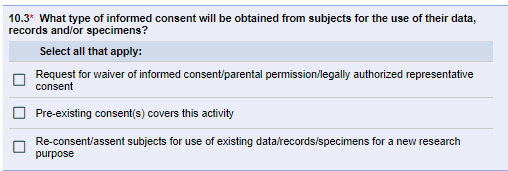
The IRB regulations regarding informed consent apply only to secondary use research requiring comprehensive (non-exempt) IRB review and approval. The IRB considers how the proposed secondary use meets the applicable regulatory requirements regarding informed consent. Prior consent obtained at the time of data/specimen collection often does not constitute “pre-existing consent” for secondary use research that involves identifiable data. For secondary-use studies requiring comprehensive IRB review and approval, eResearch Section 10.3 asks what the consent provisions are.
HIPAA Privacy Rule regulations apply to access of PHI for research purposes regardless of the IRB regulatory level (comprehensive, exempt, ‘not regulated’). HIPAA does not apply to data coming from international sources. However, General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and other similar international guidelines might apply. For all studies involving PHI, Section 25-1, question 25-1.3 asks about the HIPAA authorization provisions.

For data/specimens obtained in prior research studies, the applicable language of the informed consent document at the time the materials were obtained becomes important with respect to future research use.
Research and clinical consents often provide some notice about the possibility of future research use. Most frequently, such notices
- do not constitute upfront consent for unspecified future research on identifiable materials
- do allow for future research on identifiable materials with IRB oversight (new consent process or IRB-approved waiver of consent)
- do allow for future research on non-identifiable materials without further permissions
A few examples:
- IRBMED Standard Informed Consent Template, section 12.2:
With appropriate institutional and regulatory permissions, your collected private information and identifiable biospecimens could be used for future research with other researchers and companies, including those in other countries, with or without your consent.In addition, after identifiers are removed from your private information and any biospecimens, the information and biospecimens could be used for future research studies by U-M and shared with other researchers or companies, including those in other countries, without your additional informed consent. - Michigan Medicine Health Information Management (level-2 login required) Form 30-10000 “Request and Consent to Medical, Surgical, Radiological or Other Procedures clause 9:
Michigan Medicine may use or retransfer these items [any excess tissues, specimens, or parts of organs] to any entity for any lawful purpose, including education and research.
B. Waiver of Consent and/or HIPAA Authorization
It is common for the IRB to approve a waiver of consent and/or waiver of HIPAA authorization for secondary use analysis without prior valid research informed consent, provided that the study team follows standard U-M HRPP Data Security Guidelines. Request a waiver of consent in Sections 10.3 and 10-3. Request a waiver of HIPAA authorization in Sections 25-1 and 25-2.
C. Upfront Consent for Unspecified Future Research (occasional)
A few research consents, usually for repositories, do constitute or include upfront consent for unspecified future research on identifiable materials. IRB applications for secondary research uses of such materials can indicate that “pre-existing consent” applies.
A few examples:
- Biospecimens received from studies that make use of the IRBMED Specialty Biorepository Informed Consent Template with Informational Sheet
- Most distributions from UMMS Central Biorepository
- Most distributions from Cancer Center Tissue Procurement Service
D. Re-contact for Re-consent (occasional)
In some cases, a “secondary use” researcher may need to re-contact original subject-donors of data/biospecimens to request a new consent.
Resources
Questions?
Contact us at [email protected] or 734-763-4768 / (Fax 734-763-1234)
2800 Plymouth Road, Building 520, Room 3214, Ann Arbor, MI 48109-2800
A list of IRBMED staff is at our website.
Edited By: [email protected]
Last Updated: April 29, 2025 11:15 AM

